Context
Since few years, we observe the rise of intermediation platforms and web services consumption used through these multitude of platforms. The fact is that intermediation environments put in relation a producer/seller with a web user/consumer to enable a transaction (sales, exchange, share of products or services) that create value. Intermediation platforms are used as tools to establish relation between stakeholders and federate them as communities, though other actors are involved in the transactions (opinion leaders, observers, private providers, public entities, etc.) with indirect interests.
A new economic model
This movement creates a “space”, a place, that induces a “new economic model” split take advantages from two precedent models:
- Network economy: “active people on a platform that take part in its construction and evolution through the interactions created on It”,
- Informational goods economy: “also called immaterial or collaborative economy that finds its economic value in informational property shared to peoples, internet users who are unable to produce it”
These (inter)mediations need to be materialized, in our case using a cloud platform, referring to informational data and specific content. In that context complementary services can enrich the value creation.
Considering the specific multi-sided characteristics of intermediation platforms, we propose an adjustment of its value chain definition: “a set of actors linked together by immaterial operations relating to informational goods which consumption involves supply, production and distribution of mediated goods or services.“
The necessary environment to create a platform that allow relations between citizens and with the city is complex and diversified. The most common propositions are based on customer relationship management model extended to citizens. This is generally materialized by a web page giving access to online procedures that tries to reference civic actions and maintain a “showcase” of the city for public actors.
This approach is poor and doesn’t address the city town “users” expectations. However, citizens and user’s experiences are complementary and constitute one of the main concerns for public municipalities and governments. This is made to encourage them to develop and promote omnichannel and interactive services.
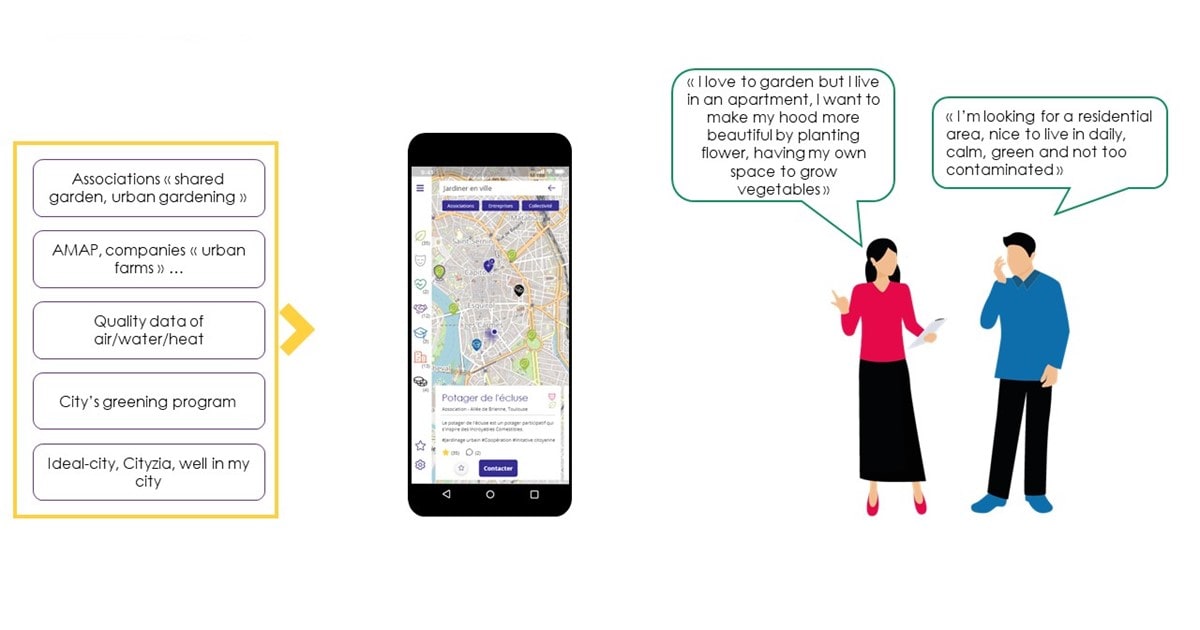
These new consumption habits highlights requirements for autonomy, time saving, life conditions simplifications and daily accountability from city’s users and citizens that constitute the ground of our proposition.
Establishing connections between users and the right city’s services
The mission of BL.Conecta is clearly to build bridges across communities in the city. The innovative value proposal can be defined as “an open window on the city”, globalizing the existing services while and localizing them in each territory. Its added value resides in its dynamic and automatized intermediation capacity to establish relations between city’s actors from a vertical perspective (between public or private services and users) and horizontal projection (between citizens and users). “The main value of this new economy is its potential for companies or individual to easily access to workers, goods and services exactly when it’s needed for a low cost” (Nicot 2017).
This context considers city’s users as producers and consumers of services. City’s services can be developed by:
- The community
- A service provider and implemented by the community
- A service provider/association
- A service provider/an association and implemented by city’s users
- A city’s users
For city’s managers, this transformation process of the territories engages them to redesign their services proposals. They must conceive and provides more adapted services to the user’s requests. To proceed they can collaborate with private solutions that can act as service’s creator or strategic adviser. This dynamic induces an evolution of the urban economic model turning the linear city’s value chain into a complex urban ecosystem where communities are competing to position themselves (Baraud-Serfaty et al. 2020).
We propose a “systemic vision” of the city that highlights the social dimension of the digital economic model. However we have to question the positioning of services intermediation digital platforms in the cities and the added value of our solution BL.Conecta?
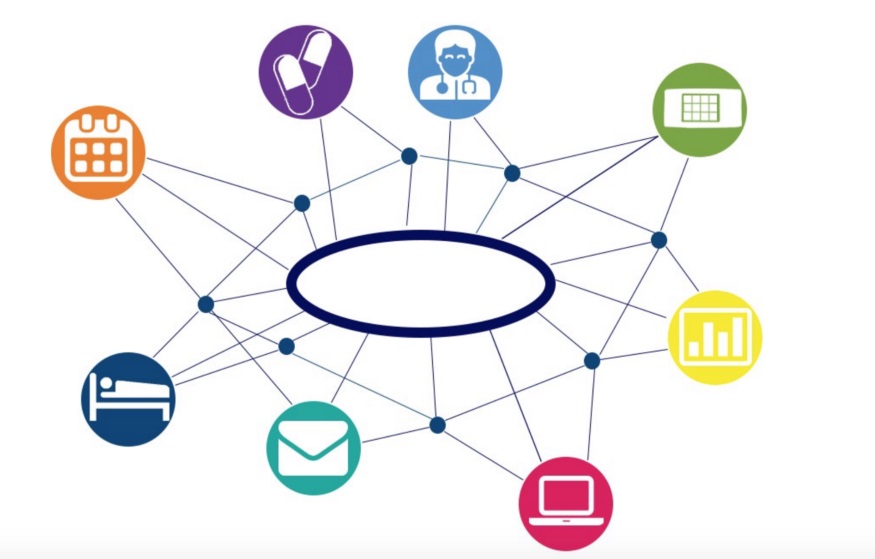
Nowadays, this phenomenon has extended to a numerous business area as shown in the figure below.
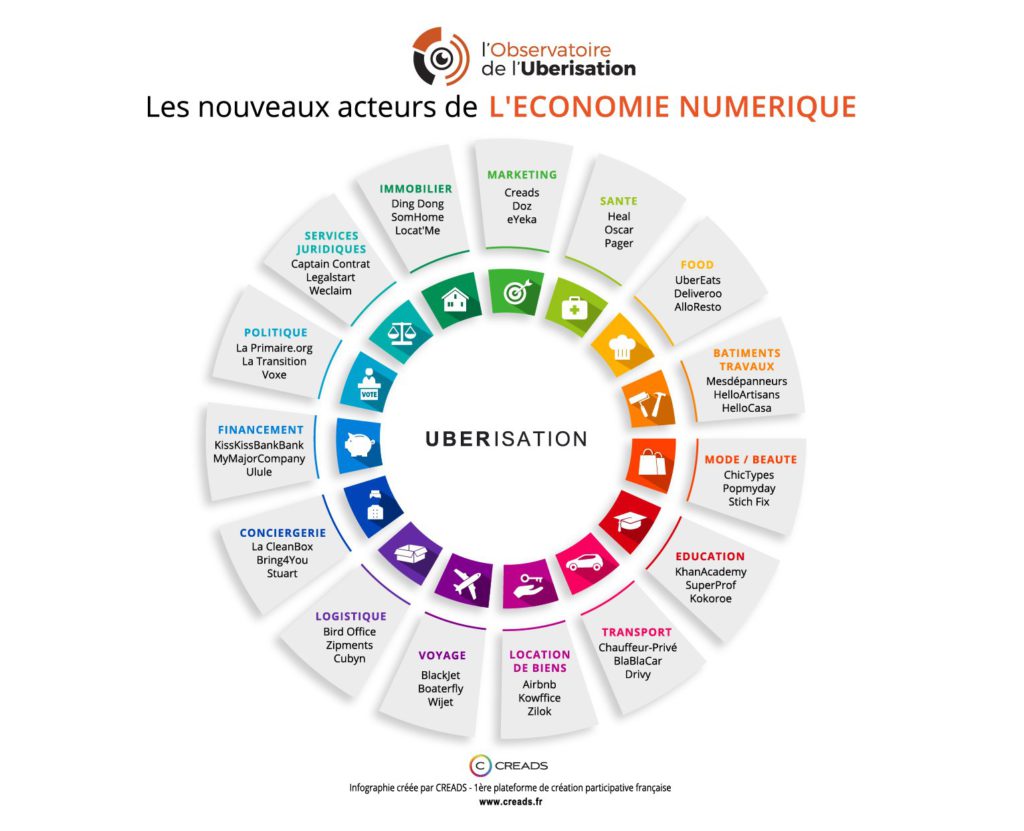
BL.Conecta is our research initiative to investigate this digital “space”, that is already served by several technologies. This economical environment is structured around three side:
- The first side links city’s users with operators offering services of the city
- The second side links communities to operators offering their services
- The third side links partners (association, industrial, collectivity, individual) offering their services directly to the operator
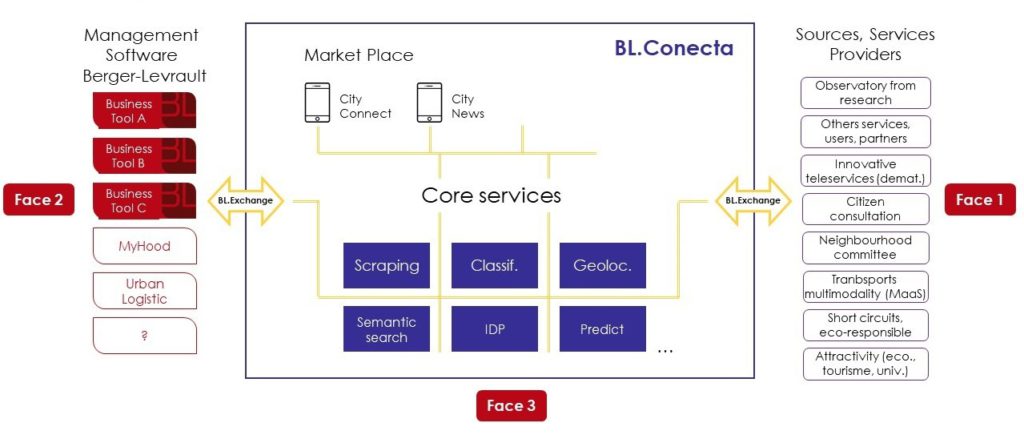
In this context, BL.Conecta is positioned as an innovative solution proposal to :
- Centralize at the same place the entirety of city’s services, providers and buyers interested in one or several exchanges through the platform
- Optimize information relevance and its rapid accessibility
- Strengthen exchange coherence between actors that brings activities in the cities and transform it
- Promote a collaborative economy
BL.Conecta mains stakes resides in its capacity to propose an hybrid intermediation, cross-sectoral and customizable, able to specify and update answers related to specific queries. These demands are tightly related to the needs and profiles of users and are intended to be compatible with a model that gets benefits from informational goods and network economies. This is furthermore produced without introducing a complex constructive information system but, instead, exploiting network infrastructures. BL.Conecta establishes relations between the different city’s actors depending on their context (localization, profile, needs…).
How does it works ?
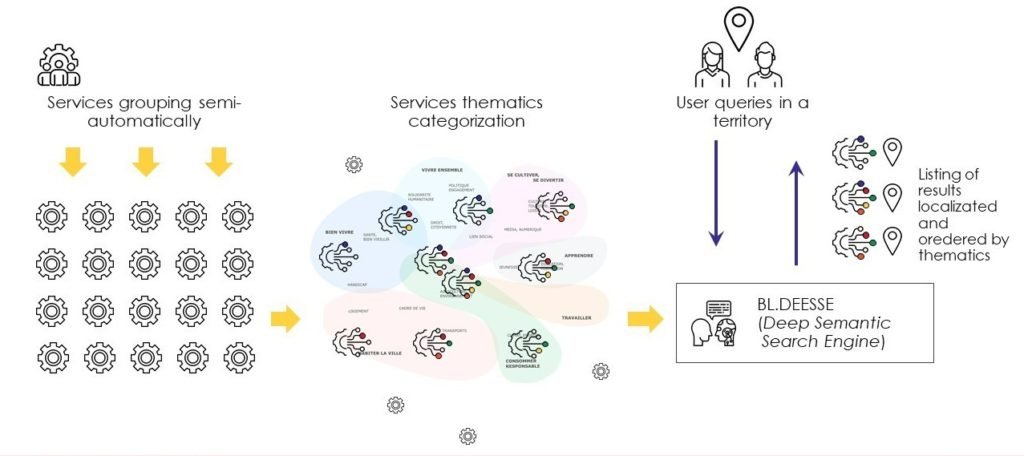
To propose the right service to the citizen or city’s users, BL.Conecta groups manually or semi-automatically the different services, it adds value to the data (localization, topic, tag, description, etc.), it materializes services transactions (by giving contact details or on a marketplace) and creates human value in the exchange between users profiles. Then, BL.Conecta services can execute on a marketplace (application) like City Connect, namely City News (internal projects).
Coming next
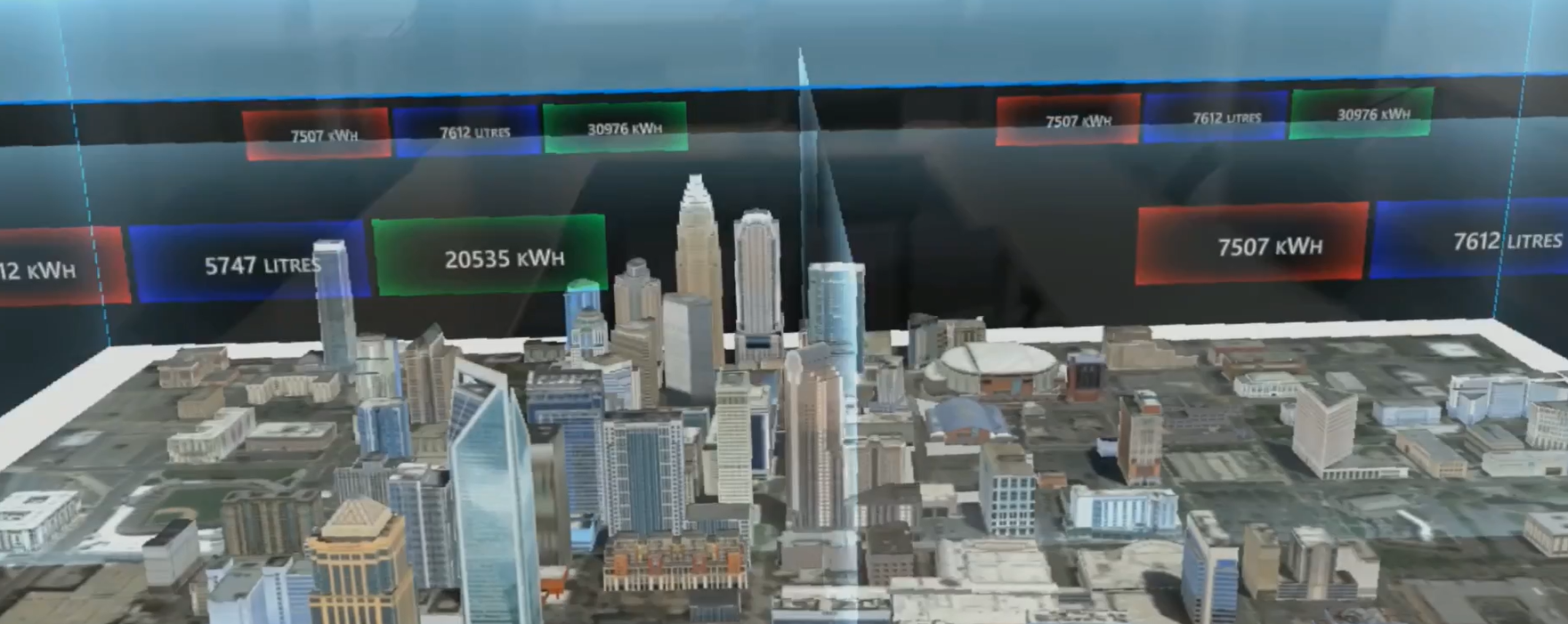
The next step of the project, by the end of April 2022, consist in creating an operational demonstrator of BL.Conecta with a first prototype of a cloud technology platform and a first application that consume BL.Conecta web services : City Connect. Below a preview of City Connect demonstrator in the video.
To be continued